WHO out with first global report on diabetes
… says 422 million adults now live with it.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) today released the first WHO Global Report on Diabetes showing that the number of people living with diabetes has almost quadrupled since 1980 to 422 million adults, with most living in developing countries.
In a press release ahead of the 2016 Word Health Day to be marked globally tomorrow (April 7), the organisation said the “driving factor” for the alarming increase include overweight and obesity and called for a global action to halt the rise and improve care people with diabetes.
According to the statement, needed measures will include expanding health-promoting environments to reduce diabetes risk factors, like physical inactivity and unhealthy diets, and strengthening national capacities to help people with diabetes receive the treatment and care they need to manage their conditions.
“If we are to make any headway in halting the rise in diabetes, we need to rethink our daily lives: to eat healthily, be physically active, and avoid excessive weight gain,” says Dr Margaret Chan, WHO Director-General. “Even in the poorest settings, governments must ensure that people are able to make these healthy choices and that health systems are able to diagnose and treat people with diabetes.”
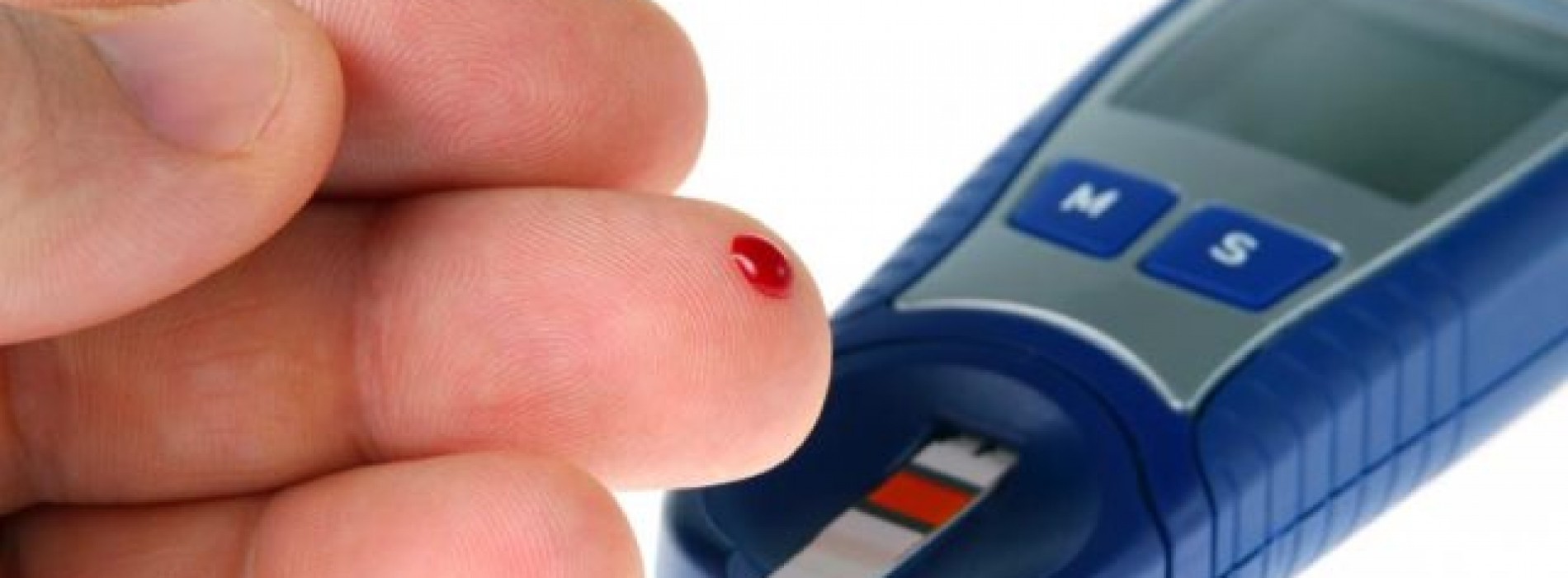
Diabetes is a chronic, progressive noncommunicable disease (NCD) characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose (blood sugar). It occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough of the insulin hormone, which regulates blood sugar, or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces.
Key findings from the “Global report on diabetes”:
• The number of people living with diabetes and its prevalence are growing in all regions of the world. In 2014, 422 million adults (or 8.5% of the population) had diabetes, compared with 108 million (4.7%) in 1980.
• The epidemic of diabetes has major health and socioeconomic impacts, especially in developing countries.
• In 2014, more than 1 in 3 adults aged over 18 years were overweight and more than one in 10 were obese.
• The complications of diabetes can lead to heart attack, stroke, blindness, kidney failure and lower limb amputation. For example, rates of lower limb amputation are 10 to 20 times higher for people with diabetes.
• Diabetes caused 1.5 million deaths in 2012. Higher-than-optimal blood glucose caused an additional 2.2 million deaths by increasing the risks of cardiovascular and other diseases.
• Many of these deaths (43%) occur prematurely, before the age of 70 years, and are largely preventable through adoption of policies to create supportive environments for healthy lifestyles and better detection and treatment of the disease.
• Good management includes use of a small set of generic medicines; interventions to promote healthy lifestyles; patient education to facilitate self-care; and regular screening for early detection and treatment of complications.
“Many cases of diabetes can be prevented, and measures exist to detect and manage the condition, improving the odds that people with diabetes live long and healthy lives,” says Dr Oleg Chestnov, WHO’s Assistant Director-General for NCDs and Mental Health. “But change greatly depends on governments doing more, including by implementing global commitments to address diabetes and other NCDs.”
These include meeting Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target 3.4, which calls for reducing premature death from NCDs, including diabetes, by 30% by 2030. Governments have also committed to achieving 4 time-bound national commitments set out in the 2014 UN General Assembly “Outcome Document on Noncommunicable Diseases”, and attaining the 9 global targets laid out in the WHO “Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of NCDs”, which include halting the rise in diabetes and obesity.
“Around 100 years after the insulin hormone was discovered, the “Global report on diabetes” shows that essential diabetes medicines and technologies, including insulin, needed for treatment are generally available in only 1 in 3 of the world’s poorest countries,” says Dr Etienne Krug, Director of WHO’s Department for the Management of NCDs, Disability, Violence and Injury Prevention. “Access to insulin is a matter of life or death for many people with diabetes. Improving access to insulin and NCD medicines in general should be a priority.”
Activities marking the 2016 World Health Day began yesterday in Nigeria with a Media Roundtable organised in Lagos by NHO, supported by multinational pharmaceutical and diagnostic company, Roche and a leading diabetes care centre, Rainbow Specialist Medical Centre. The minister of Health, Prof. Isaac Adewole used the forum to inform Nigerians of the need to adopt healthy lifestyle to curtail the global increase of diabetes.
About author
You might also like
LBS, Bloom others move to achieve drug security with new research study
Launch new research study to tackle these challenges In the light of the gaps identified in response to the COVID-19 pandemic in Nigeria and the fact that
COVID-19: Chevron donates PCR Lab to Delta State
also hands over Surgical Theatre/Consulting Rooms Chevron Nigeria Limited (CNL), operator of the joint venture between the Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation (NNPC) and CNL (NNPC/CNL JV), has donated a Polymerase
Health Journalists urge FG to fully implement National Health Act
• Seek allocation of 1% Consolidated Revenue Fund for health sector ABUJA – Health Correspondents, under the aegis of Association of Nigeria Health Journalists (ANHEJ) have appealed to the Federal






0 Comments
No Comments Yet!
You can be first to comment this post!